Documentation
Applications for electricity meters
Introduction
Electricity meters can be integrated in many places and fulfil different purposes in the cFos Charging Manager. The cFos Power Brain Wallbox and the integrated cFos Charging Manager (also available separately for Windows/Raspberry Pi) support all the types of electricity meters listed below
S0 electricity meter: The simplest and cheapest type of electricity meter. When connecting the S0 output, attention must be paid to the polarity, as nowadays it is usually a semiconductor output that only conducts in one direction. Use a twisted two-wire connection for this. If you do not register any pulses, you must swap the wires at the S0 input. An S0 current meter is supplied with our cFos Power Brain Wallbox. This can be used universally, e.g. for measuring charging power, home consumption or the generation power of your solar system. Modbus electricity meter: Electricity meter with support for the Modbus RTU protocol. The cFos Power Brain Wallbox has an RS-485 connection for Modbus RTU. For Raspberry Pi or Windows PC you need an RS-485 adapter (e.g. our Modbuskit. Smart Meter: Often installed in photovoltaic systems. This is usually a bidirectional meter that is connected to the grid transfer point and can measure whether you are drawing or feeding in electricity. These meters usually speak Modbus TCP, i.e. if your photovoltaic system is connected to your home grid, you can address this meter directly.
Note:
There are phase-resolved and non-phase-resolved electricity meters. Phase-resolved electricity meters count the electricity on each individual phase.
Meters with bidirectional measurement can distinguish consumption and feed-in. A bidirectional electricity meter at the grid reference point is recommended if you want to charge solar surplus (see below) or have an overview of your electricity feed-in/consumption for your entire house with photovoltaic system.
Mains reference
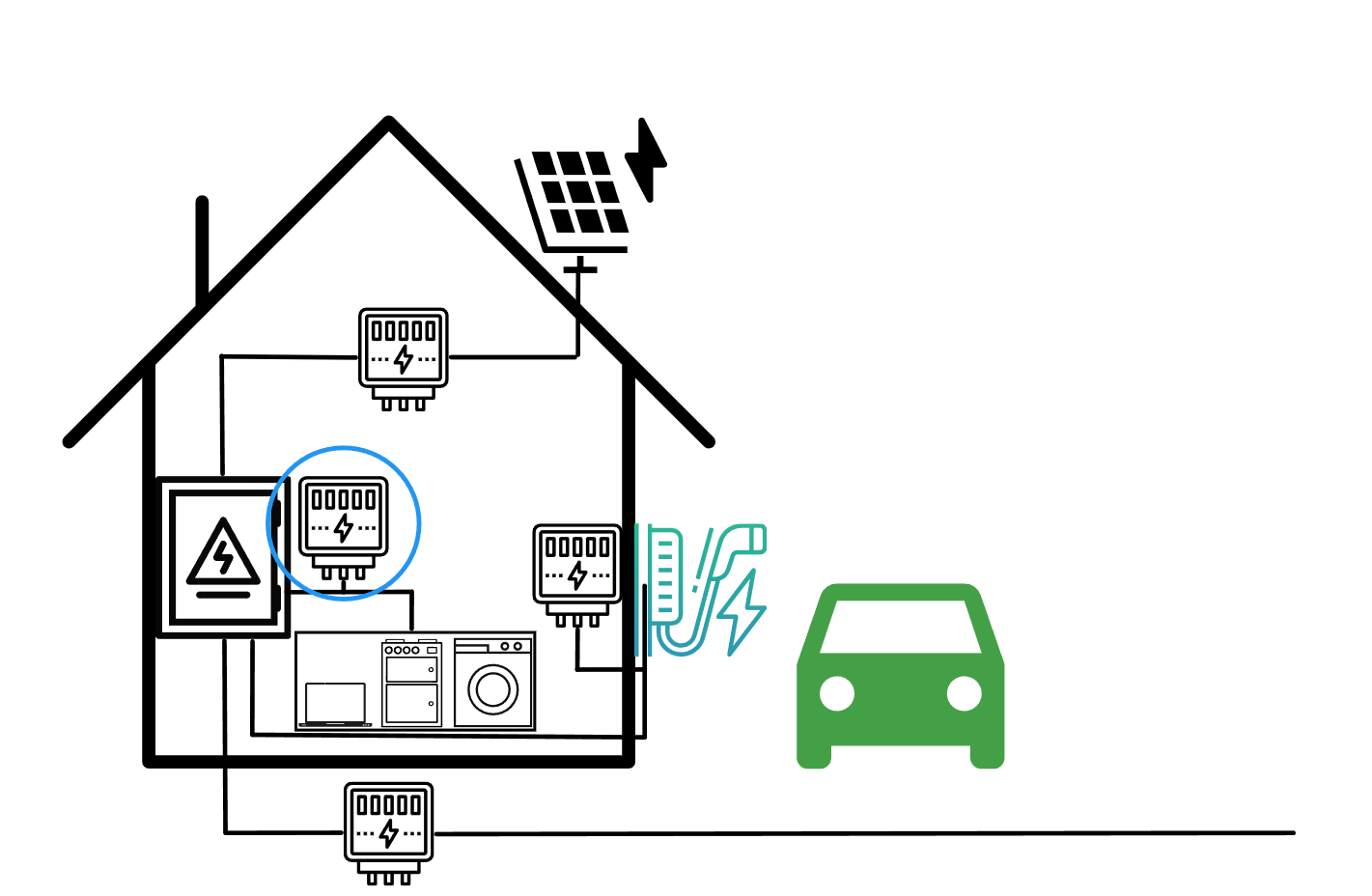
You connect the electricity meter to the grid transfer point. The cFos Charging Manager can then use this meter to determine the consumption or electricity generation of your photovoltaic system and calculate the solar surplus. If you have a photovoltaic system, you need a bidirectional electricity meter to charge solar surplus. Alternatively, you can use the consumer-generator measuring method, i.e. you install corresponding meters for all consumers and generators.
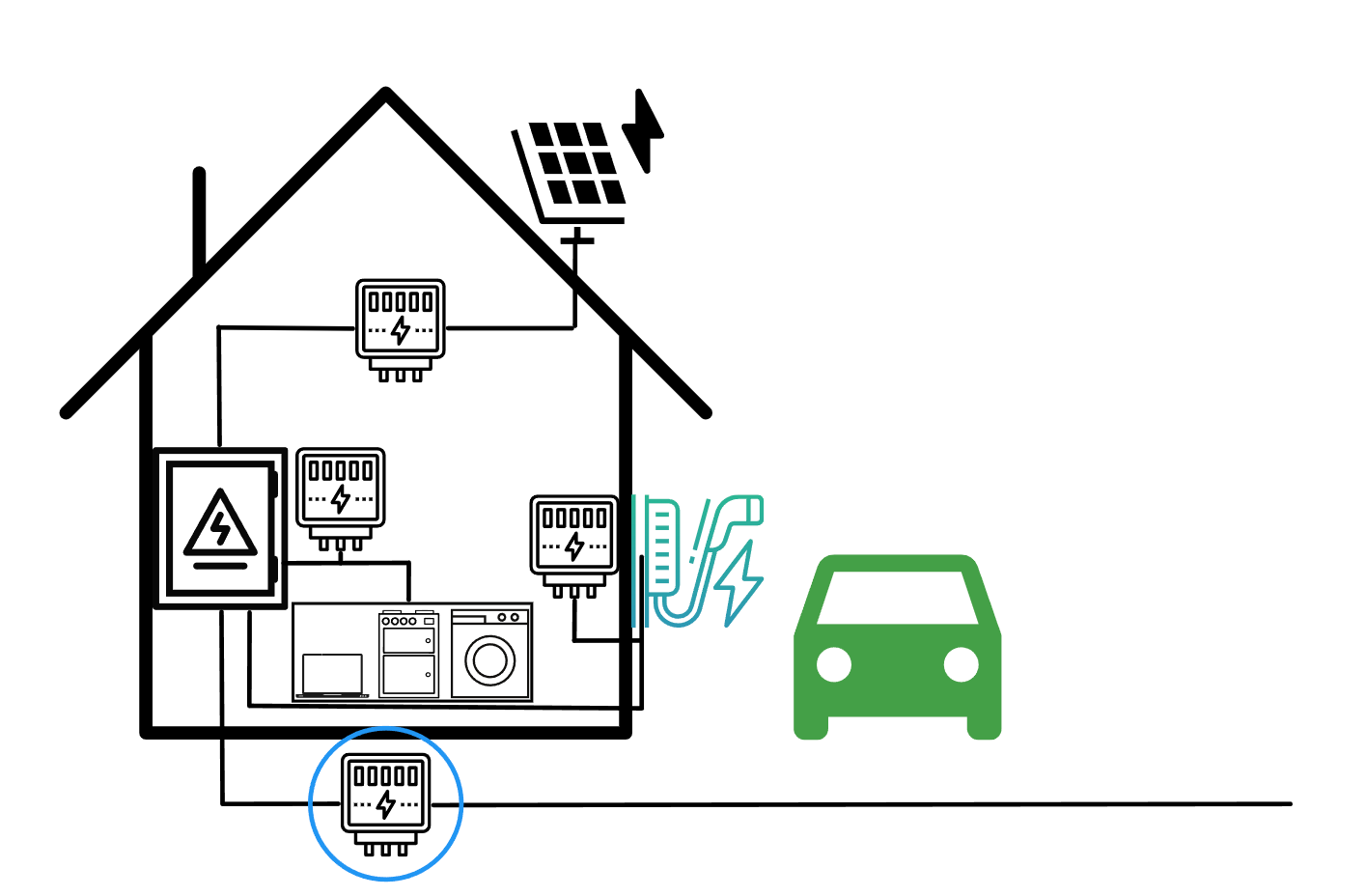
Consumption from electric car/upgrading of third-party boxes
You install the electricity meter directly in the cFos Power Brain Wallbox or connect the electricity meter behind any EVSE without an electricity meter. This allows you to keep an eye on the electricity consumption of a single EVSE. If you add an EVSE without an electricity meter to the cFos Charging Manager, you can connect an electricity meter behind this EVSE. You can then add this as a device in the cFos Charging Manager and attach it to the EVSE in the EVSE settings. For the cFos Charging Manager, a EVSE with a meter attached appears like a EVSE with an integrated meter. The cFos Charging Manager can then respond to the actual charging power of the car and thus charge intelligently.
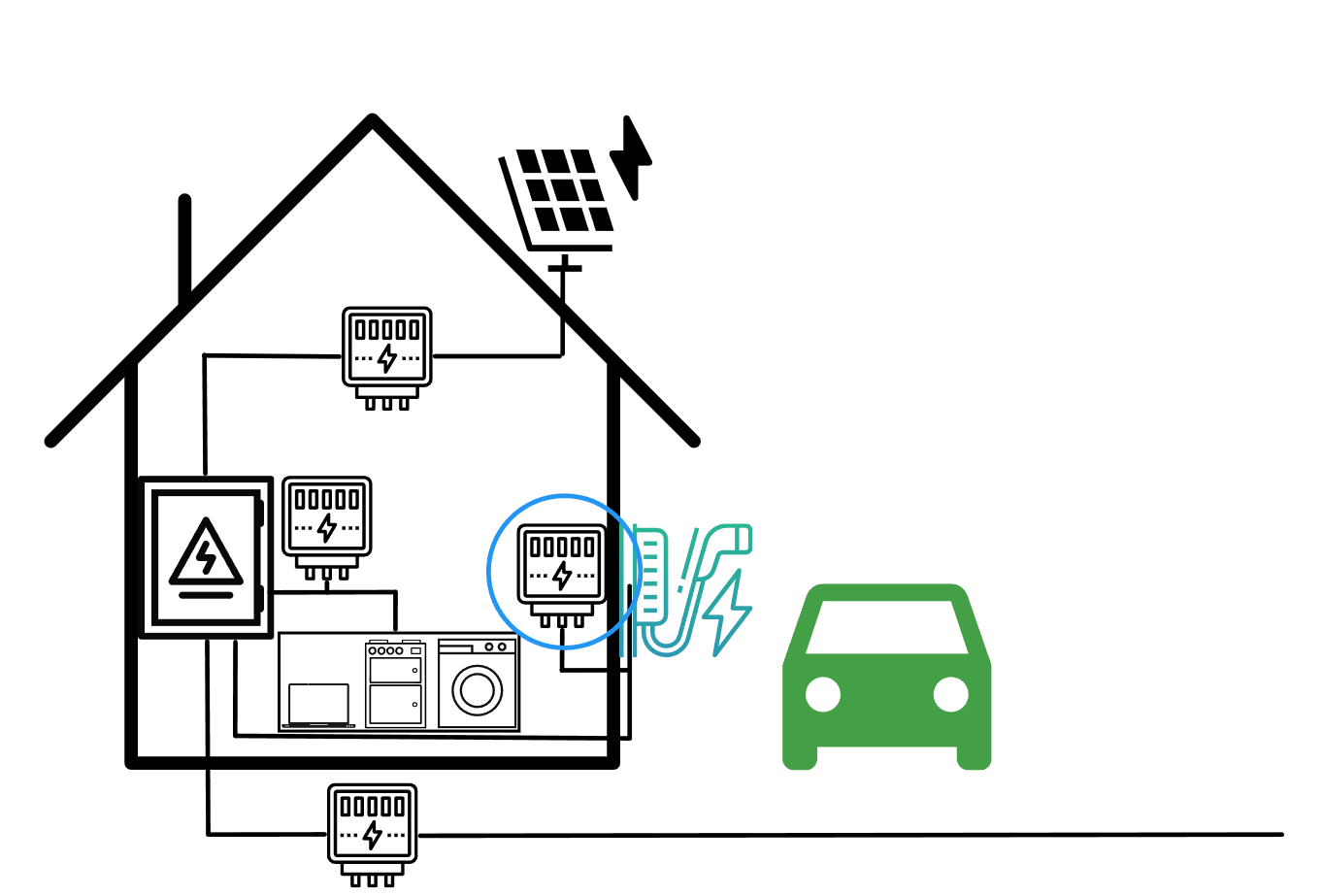
Dynamic charging current control with consideration of domestic consumption
You connect the electricity meter so that you measure the electricity consumption of the house without the cFos Power Brain Wallbox. The cFos Charging Manager will then reduce the charging power of your EVSE during load peaks to prevent overloading. This also works with multiple EVSEs. Alternatively, you can also set a fixed amount of power available to the house in total in the cFos Charging Manager and allocate a fixed buffer. With an electricity meter, the load distribution works dynamically and you can reduce your buffer. Dynamic charging current control with S0 electricity meter